RAuger-1
Beside the developement of CODALEMA in Nançay (at the time in its 2nd version CODA2 using a cabled array of fat dipoles), the Astroparticle group of Subatech was getting involved in RAuger-1, the first proposal to use the radio detection technique on the Pierre Auger Observatory site (Malargüe, Argentina), together with the Auger team of the LPSC Grenoble.
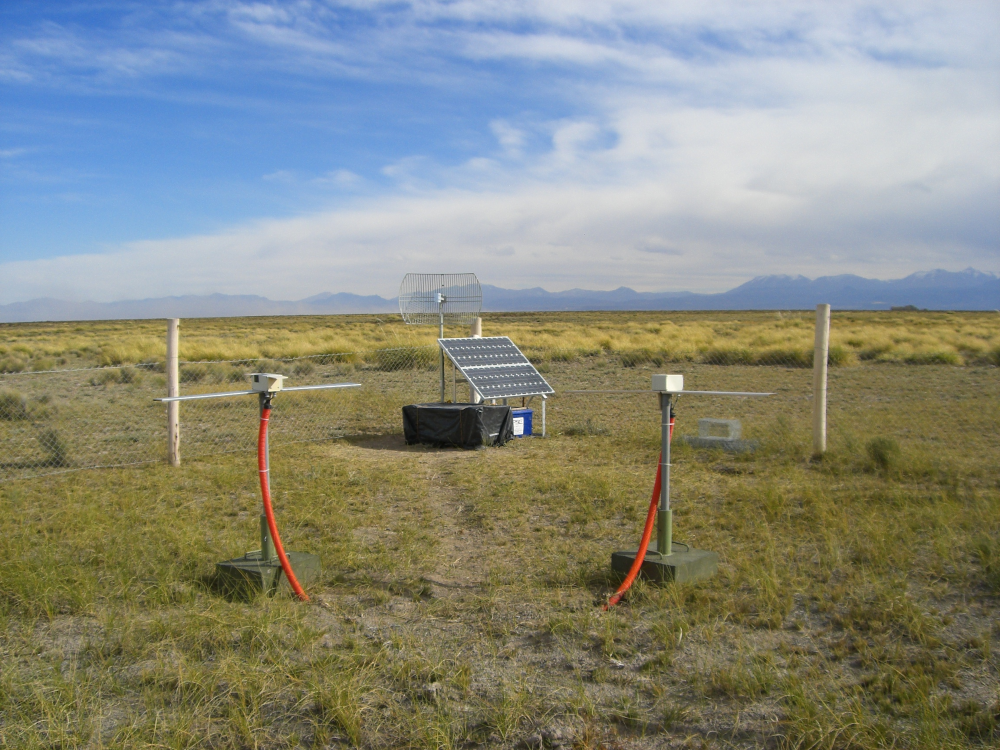 A RAuger-1 radio-detection station with its two dipole antennas and, in the back, the solar panels, the electronics box (covered by a black plastic sheet) and the WiFi antenna pointing toward the CLF.
A RAuger-1 radio-detection station with its two dipole antennas and, in the back, the solar panels, the electronics box (covered by a black plastic sheet) and the WiFi antenna pointing toward the CLF.
Considering the large areas to be instrumented, using cabled antennas was not possible on the site of Auger. The two groups thus developed the first prototype of a completely autonomous radio detection station. Built with mostly only on-the-shelf components, these stations were equipped with solar panels and batteries for power supply, a Wifi dedicated network for communication and data transmission, and used the yet well-known fat dipoles of CODALEMA as radio detection antennas. This effort lasted 4 years, and the remarkable results obtained with this modest set of antennas was continued with the second generation of autonomous station which was installed at the same time on CODALEMA (RAuger-2). These initiatives were part of the international effort aiming at developping radio at Auger, which started in 2009 and was concretized in 2013 with the large scale AERA engineering array.